Cnidaria: Rugose corals
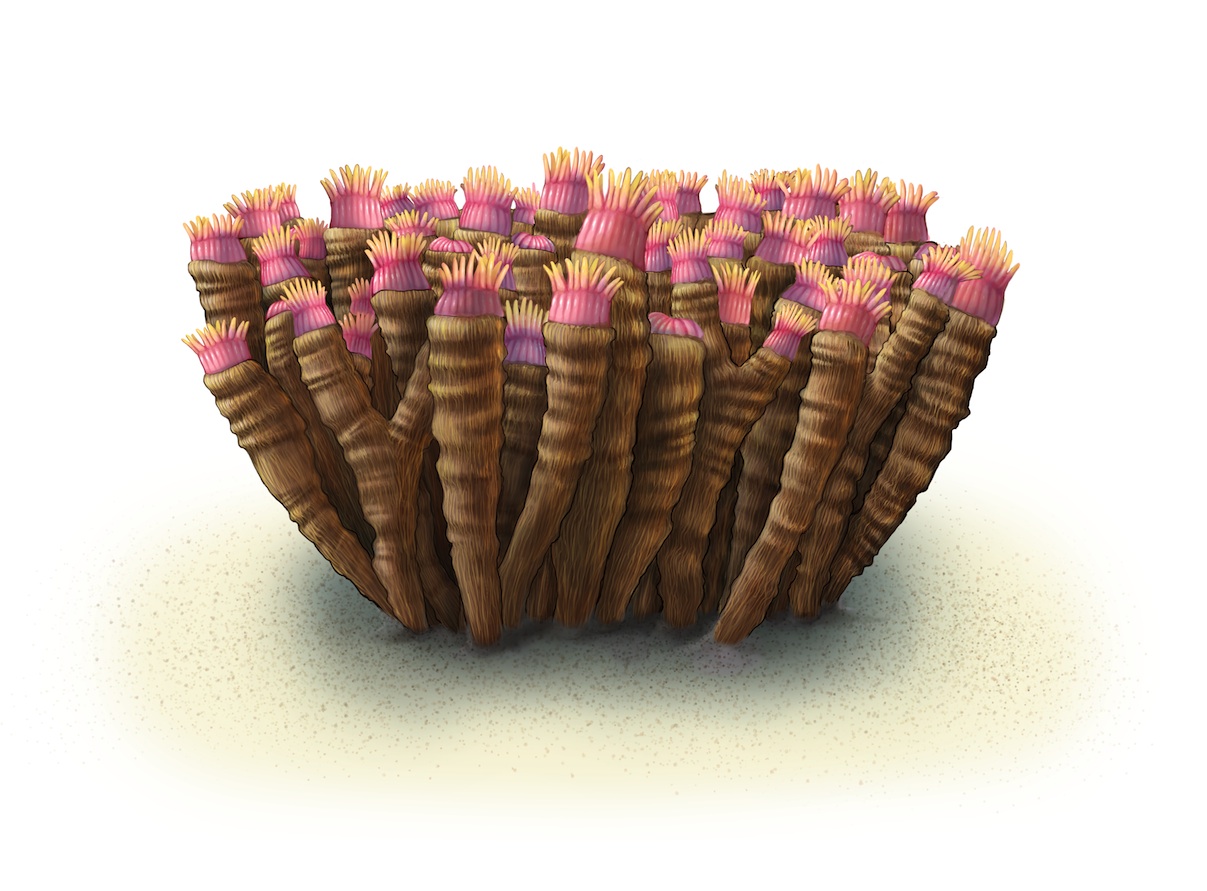
RUGOSE CORALS are extinct, but they are related to modern corals, which live only in seawater. The animal within rugose corals resembled a modern sea anemone and captured small animals and other food particles with a ring of tentacles surrounding a mouth. Rugose corals included both solitary forms, where the coral animal was housed in a cup-shaped skeleton (figures 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b), and colonial forms, where many coral animals lived together in individual spaces within the skeleton (figures 1a, 1b). | At least 13 species of rugose corals lived in the Silurian reefs of Wisconsin, and the three species shown above have been reconstructed in the diorama. Solitary rugose corals represent dwellers, and colonial rugose corals were a minor type of reef constructor.
Kingdom Animalia:
Phylum: Cnidaria:
Class: Subclass: Order: Family: Genus and species
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Amplexidae: Amplexus sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Acervulariidae: Diplophyllum sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Cyathophyllidae: Cyathophyllum sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Cyathaxoniidae: Cyathaxonia sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Eridophyllidae: Eridophyllum sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Halliidae: Blothrophyllum sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Ketophyllidae: Dokophyllum sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Kyphophyllidae: Strombodes sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Lindstroemiidae: Lindstroemia sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Lithostrotionidae: Diphyphyllum sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Ptychophyllidae: Ptychophyllum sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Pycnostylidae: Pycnostylus sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Zaphrentidae: Zaphrenthis sp.
Anthozoa: Rugosa: Stauriida: Entelophyllidae: Entelophyllum strictum





